All of it begins with a seed. Accumulating seeds out of your crops will propagate extra life from what you have already got.
Completely different plant species require different strategies of seed assortment. Under are some suggestions that will help you perceive crops’ particular needs and wishes when accumulating their seeds!
The next is an excerpt from The Ecological Gardener by Matt Rees-Warren. It has been tailored for the online.
Accumulating Seeds: Getting Began
Accumulating seed is definitely one in every of my favorite gardening duties, as I really like to take a look at the minuscule seeds in my hand and marvel how nature transforms from only one seed into the mature plant standing earlier than me.
Upon getting collected the seed, you should determine the place you’re probably to sow it subsequent, as this can affect how the seed ought to be stored.
In nature, the seed will lie on the bottom from the second it’s launched to attend for germination within the spring or possibly even a few years therefore, till the best circumstances come up.
Scattering Seed
We are able to replicate this by merely broadcasting (scattering) the seed, nonetheless connected to the stems, the place we want them to develop with out even needing to gather the seed in any respect – this works effectively for biennials like foxgloves.
Or, we are able to gather the seed in the best way described in Accumulating Seed and select to both broadcast it within the autumn or maintain some again for seeding within the spring. In that case, some data of seed dormancy is required.
Climate Issues
Stratification and Scarification
Many wild species produce seeds that depend upon specific climate patterns and occasions to be able to germinate on the optimum time for his or her survival.
These embody frosts, heavy rains, low mild ranges and fluctuating temperatures.
Dormancy is an evolutionary adaptation that stops seeds from germinating if these circumstances should not met, so if we retailer seeds inside and attempt to sow within the spring, they received’t produce crops.
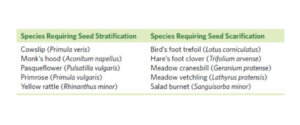
Stratification and Scarification
Due to this fact we should use a course of referred to as stratification to be able to replicate this wild dormancy interval.
One of the best ways to attain that is to position the seed inside a barely damp medium, corresponding to very gritty compost or damp paper, seal it in a jar and place it within the fridge or freezer for a time frame – usually 6–12 weeks. Some species require additional manipulation, referred to as scarification (see desk 3.3).
This entails breaking the arduous outer husk of the seed by both reducing or crushing, then permitting the inner embryo to interrupt out and germinate.
Lastly, if we’re solely looking for to retailer the seed, say till sowing the next autumn, then it’s greatest to maintain the seed fully dry in a sealed jar within the fridge or a darkish cabinet.
Sowing Seeds

Accumulating seed is among the nice pleasures of the gardening 12 months.
If the seed has been by way of the aforementioned processes, then come late winter or early spring it may be sown into pots or trays in a greenhouse or on a windowsill. If the seeds are small, then broadcasting them into trays is the best.
After they break by way of and kind seedlings, you may skinny out round half to permit the others to develop robust and wholesome. As these seedlings develop larger, tease out and place them right into a small pot to develop on additional.
If the seeds are giant sufficient to deal with individually, place them one after the other into small pots and develop on till they are often transplanted into bigger pots or out within the floor.
Keep in mind to make use of low-nutrient soil to start with and transfer progressively up into larger vitamins because the crops progress – for instance, from leafmould and sand to compost and loam.
Accumulating Seeds
Accumulating seed isn’t as simple because it appears; it takes timing, expertise and judgement to gather on the excellent stage of ripeness.
1. As soon as the plant has flowered, look ahead to the stem and the seedhead to brown and ripen.
2. Gather on a dry day. Lower the entire stem off with the seedhead connected and place in a paper bag or one thing comparable.
3. Take the stem inside and thoroughly extract the seeds on a desk with white paper unfold out on top – seeds could be small so the paper will make it easier to detect them once they fall.
4. Upon getting launched all of the seeds, gather them up and place them in small envelopes or sachets, then label them.
Really useful Reads
Maintaining Seeds Organized: Saving & Storing
8 Seed Saving Myths


